Scientists have converted plastic water bottles into a vanilla flavoring by using genetically-engineered bacteria. The production of the chemical as been heralded as a positive way to encourage recycling by some.
Plastics Converted to Vanilla Flavoring Vanillin
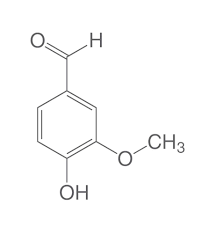
The Guardian reported that plastic water bottles were converted into the already-popular flavoring by using a genetically-engineered bacteria. Previously, researchers managed to employ a mutated enzyme to convert polyethylene terephthalate polymer found in discarded plastic bottles into terephthalic acid (TA).
Now, scientists have used the bacteria to turn TA into vanillin.
The genetically-engineered bacteria was E.Coli, according to USA Today.
Some have lauded the effort to repurpose the discarded plastic — seeing as plastic loses 95% of its value after its first use and a mere 14% of plastic is recycled.
Vanillin is already mostly derived from fossil fuels with 85% of its 37,000 ton annual demand coming from chemicals synthesized from fossil fuels.

Scientist, Joanna Sadler, of the University of Edinburgh, who conducted the study, said: “This is the first example of using a biological system to upcycle plastic waste into a valuable industrial chemical and it has very exciting implications for the circular economy.”
While Stephen Wallace, who was also part of the team at the University of Edinburgh, said: “Our work challenges the perception of plastic being a problematic waste and instead demonstrates its use as a new carbon resource from which high value products can be made.”
According to The Guardian: “Vanillin is used widely in the food and cosmetics industries and is an important bulk chemical used to make pharmaceuticals, cleaning products and herbicides.”
In the past, we have talked at length with the problems with microplastics and endocrine disruptors found in plastics.
Microplastics are now found in honeybees, and, if humans were to disappear tomorrow, microplastics would still be a part of nature.
Microplastics: Health Implications
A baby fish full of microplastic balls
We already know that the actual physical effects of consuming microplastics can be deadly for many species of animal. Fish, for instance, are being killed because some varieties seem to prefer eating microplastics to their normal food sources, effectively starving them. Baby fish are especially vulnerable. [R]
The implications for humans are less clear, beyond the possible contribution of microplastics to declining fish stocks and the collapse of marine ecosystems and the knock-on effects of this for us; but we can still speculate about what effects these microplastics might be having in the human body as well.
In our article on xenoestrogens, we considered the role of pthalates, in particular, to endocrine (i.e. hormonal) disruption in humans and other animals. Pthalates were first introduced on a wide scale during the 1950s, when PVC became readily available. They are used to increase plastic flexibility, and as a result have a myriad of applications: in food containers, water bottles and children’s toys, as well as foams, solvents, perfumes, pesticides, nail polish, adhesives and lubricants. Studies of pthalates have shown that prenatal exposure may cause feminisation of baby boys and be responsible for smaller penis size. [R]
Given that many if not all of these microplastics will have been treated with such substances, we can imagine that they might also act as vectors for them to enter the human body, with disruptive effects. Just how great these effects might be remains to be seen, and requires urgent research.
We do already have a number of studies on the effects of microplastics on marine life, and the findings are as dire as you might expect. In one study of female fish, the researchers found that the microplastics caused tissue damage, disrupted production of reproductive and sex-specific hormones including 17β-estradiol and testosterone and had noticeable cross-generational effects, stunting the growth of newborn fish, as well as increasing the incubation period and decreasing the rate of hatching. [R] Other studies have documented liver toxicity and various other pathologies in marine life. [R] [R]

Don’t hesitate to email us at [email protected] for personalized coaching and a client questionnaire if you’d like DEDICATED tailor-made personal training on strength training, building muscle, losing fat, developing athleticism, and more — all to your liking, lifestyle, habits, and taste!
Otherwise, don’t forget to claim your FREE eBook detailing how to lose 20lb of fat while building muscle in 12 weeks! You can claim it here.
Alternatively, you can pick up a FREE eBook on fundamental strength principles offering an introductory workout program.











